In the new era of intelligent manufacturing and advanced materials, liquid metal and precision injection molding stand as two cutting-edge manufacturing technologies, each showcasing unique technical advantages and application potential. Despite both involving material shaping, they differ significantly in material properties, processing techniques, and application scenarios. This article analyzes their differences and interconnections from five key dimensions.
1. Material Fundamentals: Core Composition and Property Disparities
1.1 Characteristics of Liquid Metal
Liquid metal, also known as amorphous alloy, exists in a liquid or semi-solid state at room temperature. Its atoms arrange in a short-range ordered but long-range disordered pattern. Zirconium-based and magnesium-based liquid metals, for instance, combine high strength (tensile strength exceeding 1500MPa), hardness, and excellent corrosion resistance. Notably, their near-zero shrinkage during solidification enables high-precision forming of complex structures, a feature beyond traditional metals.

1.2 Material Systems of Precision Injection Molding
Precision injection molding primarily uses polymers, including engineering plastics like polycarbonate (PC) and polyetheretherketone (PEEK), and biodegradable materials such as polylactic acid (PLA). These materials offer low density, chemical stability, and ease of processing. PEEK's high heat resistance makes it ideal for aerospace and medical applications, while PLA’s environmental friendliness suits sustainable product design.
2. Forming Principles: Technological Mechanisms
2.1 Liquid Metal Forming Processes
Liquid metal mainly applies die-casting and injection molding. Under high pressure, its low viscosity and high fluidity allow rapid mold filling. For smartphone frame production, liquid metal die-casting can achieve wall thicknesses below 0.1mm with high surface finish, eliminating the need for secondary processing.
2.2 Precision Injection Molding Logic
Precision injection molding exploits the thermoplasticity of polymers. Solid plastic pellets melt, then screw extrusion injects the molten material into molds. Precise control of temperature, pressure, and cooling rate ensures dimensional accuracy. In optical lens molding, temperature fluctuations must stay within ±1℃ to prevent internal stress-induced optical distortion.
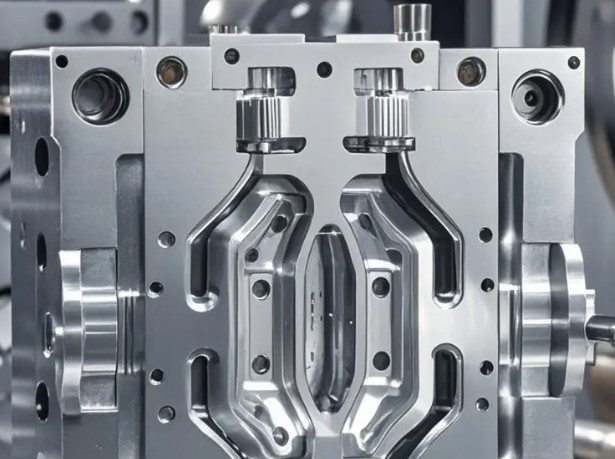
3. Process Characteristics: Precision, Efficiency, and Cost
3.1 Forming Precision and Surface Quality
Liquid metal excels in micron-level precision due to low shrinkage, suitable for intricate parts like watch gears. Precision injection molding, with optimized molds and parameters, also achieves 0.01mm-level accuracy, particularly for high-precision optical components.
3.2 Production Efficiency and Cost Structure
Liquid metal die-casting demands high equipment investment but enables fast cycle times for mass production. Precision injection molding has lower equipment costs, yet longer cooling times reduce efficiency. Additionally, liquid metal scrap recycling is difficult, while injection molding scrap can be recycled, affecting overall costs differently.
4. Application Scenarios: Domain Focus and Functional Demands
4.1 Applications of Liquid Metal
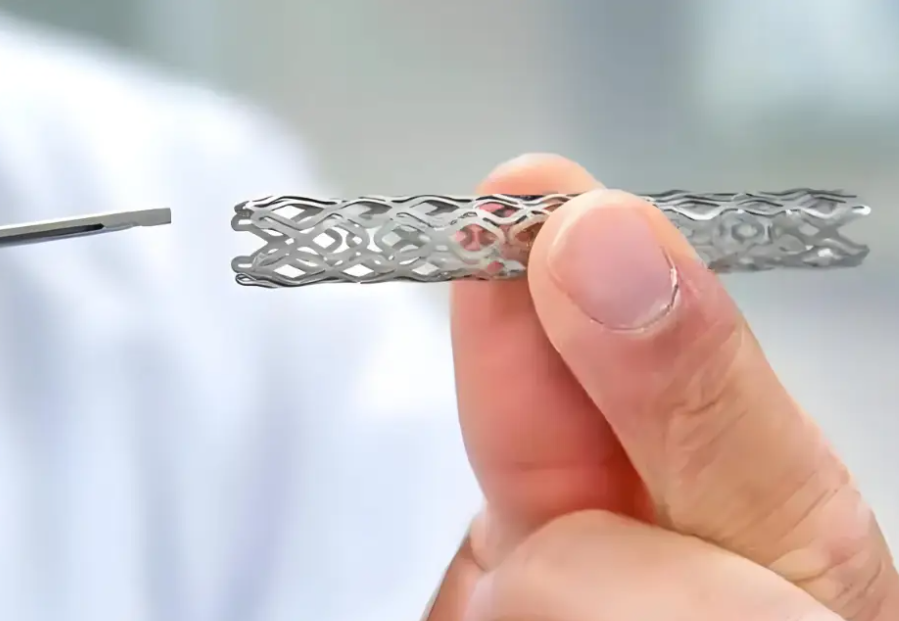
Liquid metal plays a key role in 3C products (e.g., the frame of Xiaomi MIX Alpha), aerospace (engine blade seals), and medical devices (vascular stents). Its high strength and fatigue resistance make it an optimal substitute for traditional metal parts.
4.2 Application Landscape of Precision Injection Molding
Precision injection molding applies widely across consumer electronics, automotive, and medical fields. From smartphone casings and automotive interiors to disposable syringes and dentures, biocompatible materials support personalized medical solutions.

5. Future Trends: Technological Integration and Innovation
With the development of intelligent manufacturing and digital technologies, liquid metal and precision injection molding are converging. Simulation technologies optimize process parameters for higher precision and efficiency. Hybrid manufacturing, combining liquid metal and polymers, emerges as a research focus, promising to overcome single-material limitations. For example, integrating liquid metal’s heat dissipation with polymer insulation can create safer and more efficient battery packs for new energy vehicles.




